Java Objects in Activities: Android Programming
Demonstration/guide on how to use custom plain-old Java objects inside an Activity.
Java code and outline are in this description (below).
Ideas:
———————————————
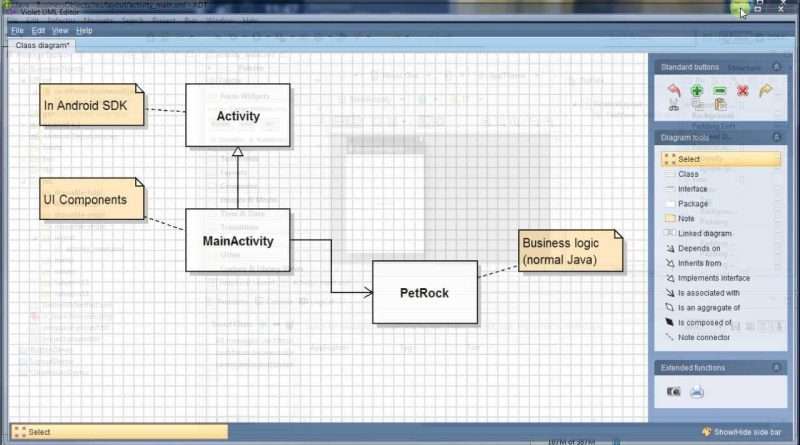
– Separate the UI from the Business Logic (BL)
– BL plain java
– UI code (Android) calls BL objects.
Steps:
———————————————
1. Design and implement BL (Java classes).
2. Instantiate BL object in UI code.
3. Call BL object from UI code (client)
enum:
———————————————
A set of possible values.
Example:
public enum Emotion {TIRED, HAPPY, SAD};
Example:
———————————————
PetRock: Generate get/set
public class PetRock {
public enum Emotion {TIRED, HAPPY, SAD};
private Emotion currentEmotion = Emotion.TIRED;
public Emotion getCurrentEmotion() {
return currentEmotion;
}
public void setCurrentEmotion(Emotion currentEmotion) {
this.currentEmotion = currentEmotion;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return « I’m feeling » + currentEmotion.toString() + « . »;
}
}
UI:
– Label for status
– 2 Buttons for Happy/Sad to change state and update UI
Function to setup each button, then refactor to one function.
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private PetRock rocky = new PetRock();
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
setupEmotionButton(R.id.btnHappy, Emotion.HAPPY);
setupEmotionButton(R.id.btnSad, Emotion.SAD);
updateUI();
}
private void setupEmotionButton(int buttonId, final Emotion newEmotion) {
Button button = (Button) findViewById(buttonId);
button.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View arg0) {
rocky.setCurrentEmotion(newEmotion);
updateUI();
}
});
}
private void updateUI() {
TextView textView = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.txtRockyFeeling);
String feeling = rocky.toString();
textView.setText(feeling);
}
}
Views :15316
android programming language